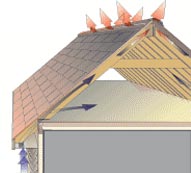
What is attic ventilation and what are its benefits?
Attic ventilation refers to an inlet and outlet system on your home that allows a constant flow of air in and out of the attic. An effective attic ventilation system provides year round benefits by keeping the attic cool during summer and keeping the attic dry during winter. A cool attic lowers energy costs because the air conditioner does not have to cool the hot attic air and the duct system is not exposed to high temperatures. During winter, the reduction of moisture protects your HVAC equipment and home against damage.
How does attic ventilation work?
An effective attic ventilation system most provide a steady, high volume of air. Air movement is created either by using natural ventilation or powered ventilation, such as a solar attic fan.
Natural Ventilation is achieved by the thermal flow and the wind. Thermal flow takes advantage of the fact that hot air rises by placing inlets in the lower part of the attic and outlets in the highest part. The wind creates a difference in pressure which drives the air out from the attic.
Powered Ventilation consists of using either a electrical or solar attic fan to exhaust air from the attic. Powered fans have to be installed carefully since they can sometimes draw cold air from the inside of the house when there is not enough intake area in the attic or when the house is not well sealed.
How much attic ventilation do I need?
The rule of thumb is 1 sq. ft. of venting area per 150 sq. ft. of attic floor, which has to be equally distributed between intake and exhaust (50% intake, 50 % exhaust). For example, a 1000 sq. ft. attic would need 1000/150 = 6.6 sq. ft. of venting area, 3.3 sq. ft. of intake and 3.3 sq. ft. of exhaust. For powered ventilation the size of the fan is obtained by multiplying the square footage of the attic by 0.7. For example, a 1000 sq. ft. attic would need 1000 x 0.7 = 700 CFM fan.

